Diabetic retinopathy represents the damage to the blood vessels of the retina with the appearance of morphological and functional damage, up to the rupture and appearance of retinal hemorrhages and macular edema, which can lead to vision loss in patients with diabetes.
What are the causes of retinopathy in diabetes
What are the symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
The diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy
Treatment of diabetic retinopathy
Treatment of diabetic retinopathy
What is diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy represents the damage to the blood vessels of the retina with the appearance of morphological and functional damage, up to the rupture and appearance of retinal hemorrhages and macular edema, which can lead to vision loss in patients with diabetes.
The condition can be encountered in medical practice in the form of:
- Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy with generally asymptomatic evolution and good prognosis
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy manifests itself through retinal neovascularization (formation of new, abnormal vessels in the retina) and represents the most advanced stage of the disease with a reserved prognosis
What are the causes of retinopathy in diabetes
The main cause of the appearance of retinopathy in diabetic patients is represented by the harmful effect of hyperglycemia on the microvascularization of the whole body, but other favorable factors have been identified which, in association with diabetes, cause pathological changes in the retinal vessels:
- Hypertension
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
- Unbalanced chronic diabetes
What are the symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
The pathological processes that determine the appearance of retinopathy in diabetics require long periods of action, the patients being asymptomatic in the initial stages of the disease, the condition becoming clinically manifest only in the advanced stages of evolution. The main symptoms of diabetic retinopathy are represented by:
- Blurred vision
- Affecting the degree of color perception
- The sensation of floating bodies in the eyes (points that appear in the visual field)
- Decreased visual acuity at night
- Sudden and total loss of vision
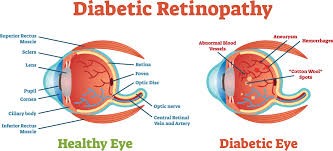
Complications of diabetic retinopathy are represented by:
- Hemorrhage of the vitreous body due to retinal tears, causes photophobia (sensitivity to light) and in severe forms can lead to vision loss
- Detachment from the retina due to the pressure exerted by the scar tissue is manifested by the perception of bright flashes or strips of light and a significant decrease in vision
- Glaucoma due to fluid accumulation and increased intraocular pressure with destruction of the optic nerve and blindness
The diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy
The diagnostic methods of diabetic retinopathy include, in addition to the patient’s anamnesis and the clinical examination performed by the ophthalmologists in both eyes, the measurement of the visual acuity of the intraocular tension and the anterior eye pole and the following paraclinical investigations:
- Ocular ultrasonography of the posterior pole
- Angio fluorography to determine the degree of damage to the retina
- Retinal tomography
Treatment of diabetic retinopathy
The medicinal treatment of diabetic retinopathy is auxiliary to surgical interventions, being used to slow down the pathological processes that determine the progression of the condition, being represented by vascular tonics for strengthening the retinal capillaries, lipid-lowering agents and pharmacological substances that help the resorption of microhemorrhages.
The surgical treatment of diabetic retinopathy is performed with the help of:
- Laser coagulation – laser treatment for macular photocoagulation and pan photocoagulation by which the pathological neoformation micro vascularization is obstructed
- Vitrectomy (removing the vitreous body and replacing it with liquid or gas)
Treatment of diabetic retinopathy
The medicinal treatment of diabetic retinopathy is auxiliary to surgical interventions, being used to slow down the pathological processes that determine the progression of the condition, being represented by vascular tonics for strengthening the retinal capillaries, lipid-lowering agents and pharmacological substances that help the resorption of microhemorrhages.
The surgical treatment of diabetic retinopathy is performed with the help of:
- Laser coagulation – laser treatment for macular photocoagulation and pan photocoagulation by which the pathological neoformation micro vascularization is obstructed
- Vitrectomy (removing the vitreous body and replacing it with liquid or gas)
Find out more:
- The prevalence of diabetic retinopathy among adults in the United States. – https://europepmc.org/article/med/15078674
- Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy – https://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/38/10/1203.short
- Diabetic retinopathy – https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00125-002-0990-7


